This is the season to protect against Lophodermium needlecast
Editor’s note: This article is from the archives of the MSU Crop Advisory Team Alerts. Check the label of any pesticide referenced to ensure your use is included.
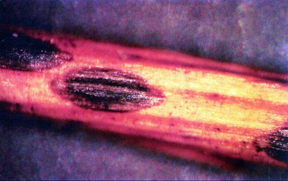
Management of Lophodermia needlecast disease of Scotch and red pine, caused by the fungal pathogen Lophodermium seditiosum, is slightly different than the needlecast diseases found on Douglas fir and spruce. This disease can kill red pine seedlings and causes browning and massive amounts of needle loss on Scotch pines. Scotch pines infected with this disease have needles with brown spots surrounded by yellow margins, yellow needles or brown needles, especially at the bottom of the tree.
Lophodermium is a severe needlecast of Scotch pine, which in some cases can cause the entire tree to brown in the spring. Even though we see the symptoms of Lophodermium in the spring, the most important time to protect trees is from the end of July through September. This is when needles are infected from spores being released by the small, shiny, football-shaped, black fruiting bodies that form on the fallen needles. The dead needles currently falling off the trees this summer (June, July and August) will provide the inoculum (spores) that will spread throughout the trees in your plantation or nursery. These spores will infect this year's crop of needles from August to October. And, even though you won't see the result of those infection events until next year, the fungus will stay in those healthy looking needles all winter until spring, when, again, those needles will begin the process of yellowing, browning and dropping off. To break this disease cycle, the time to manage this disease is in late July and throughout August, even into fall, if it stays warm and moist.
To initiate control, you must begin now. Look for needle spots and brown foliage on the lower branches of 50 or more trees scattered throughout the plantation. If ten percent of the trees are infected, consider treating the entire plantation by the first week of August. To reduce Lophodermium needlecast, remove the branches of pine from cut stumps where spores are likely to be produced. Apply a registered, preventative fungicide three or four times, once every two to three weeks from late July through October. Make sure all the older pines have been removed from windbreaks near nurseries or plantations. These pines can serve as sources of fungal spores.



 Print
Print Email
Email