Caution – danger zone!
Keeping food safe is important to reduce the risk of food poisoning. When preparing food for gatherings with family, guests or a simple meal for yourself, it is important to be alert to the temperature danger zone.
Keeping food safe is important to reduce the risk of food poisoning. When preparing food for gatherings with family and guests or even a simple meal for yourself it is important to be aware of the temperature danger zone. What is the temperature danger zone? As the name implies, the danger zone refers to the most dangerous temperature for foods, between 40 and 140 degrees Fahrenheit. This range of temperature is dangerous because it’s below the temperature at which heat destroys bacteria (above 160 degrees Fahrenheit), yet above the cooling range (below 40 degrees Fahrenheit), where the growth of bacteria is slowed.
Why the concern you might ask? This is dangerous because a single bacterium can multiply to trillions in just 24 hours when between 40 and 140 degrees Fahrenheit. This is because bacteria double approximately every 20 minutes under the right conditions: Food, moisture, oxygen and warm temperature. Many foods, with their rich supply of nutrients and moist quality, offer the perfect environment for bacteria to grow. Failing to follow these guidelines can encourage bacterial growth by providing a warm temperature, as well.
It is also important to note that certain people can have a greater risk to food poisoning if exposed to foods improperly handled. These are the very young, elderly people and those with compromised immune systems.
Michigan State University Extension and the Food Safety Inspection Service offer these critical points to keep food safe from the temperature danger zone.
Never leave food out of the refrigerator for more than two hours. Keep hot foods hot (at or above 140 degrees Fahrenheit) and cold foods cold (at or below 40 degrees Fahrenheit).
Raw meat and poultry should always be cooked to a safe minimum internal temperature – refer to the graphic United States Department of Agriculture graphic 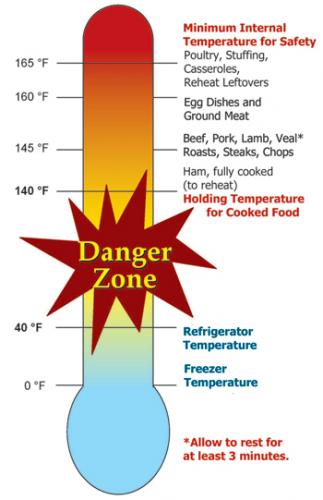
When roasting meat and poultry, use an oven temperature no lower than 325 degrees Fahrenheit. If you aren't going to serve hot food right away, it's important to keep it at 140 degrees Fahrenheit or above.
Storing leftovers: One of the most common causes of foodborne illness is improper cooling of cooked foods. Bacteria can be re-introduced to food after it is safely cooked. For this reason leftovers must be put in shallow containers for quick cooling and refrigerated at 40 degrees Fahrenheit or below within two hours.
Reheating: Thoroughly reheat foods to an internal temperature of 165 degrees Fahrenheit or until hot and steaming. In the microwave oven, cover food and rotate so it heats evenly. Use a food thermometer to determine if food has cooled to 40 degrees Fahrenheit or lower, or if it has been reheated to an internal temperature of 165 degrees Fahrenheit.
Following these food safety practices will help to ensure that food is safe and reduces the risk of food poisoning.



 Print
Print Email
Email


